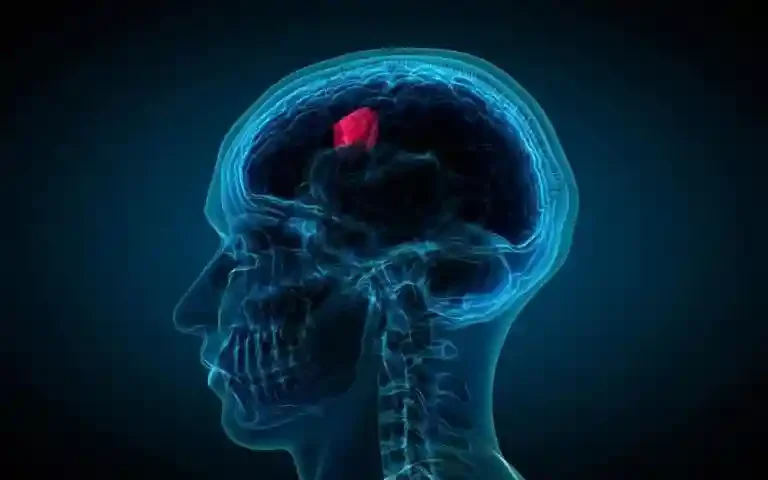
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells developing in the brain. They can be benign or malignant. The tumors can be primary brain tumors originating in the brain (Gliomas) itself or in tissues close to it, such as in the brain-covering membranes, cranial nerves, pituitary gland or pineal gland. Sometime tumor can be a secondary lesion from another cancer in the body and spreads to the brain ( Metastatic Brain Tumors) .Brain tumors can grow rapidly and affect well the function of your nervous system.
Symptoms of brain tumor include:
- New or increasingly strong headaches, blurred vision, loss of balance, confusion and seizures.
- fficulty walking, instability, muscle weakness, problems with coordination, weakness of one side of the body, or weakness of the arms and legs
- Dizziness, fatigue, or vertigo
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pins and needles or reduced sensation of touch
- Inability to speak or understand language or mental confusion
- Blurred vision, difficulty speaking, personality change, seizures, or sleepiness
Diagnosis of brain tumors can generally be carried through a neurological examination. Diagnosis can be carries though CT scans, MRI, PET scan and through biopsies. These are generally advised by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. At Wockhardt Hospitals we provide advanced imaging support for diagnosis for further evaluation and treatment.
The standard treatment for brain tumors includes surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy. In general, radiation and chemotherapy treatments are used as secondary or adjuvant treatments for tumors that cannot be managed using only surgery. However, radiation and chemotherapy may be used without surgery if the tumor is inoperable.
Neuro-Oncosurgery at Wockhardt Hospitals:
Neuro-oncology is a sub-specialization that deals with brain tumors and spinal cord tumors. These tumors can be both benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors can be divided into primary – that arise from within the brain and spine and secondary tumors – that have spread to brain and spine from other body parts, known as metastatic tumors. All types of brain and spinal cord tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the part of the brain and spinal cord involved.
With the advancement of technology (advanced microscopes, intraoperative navigation) and better investigation facilities, the morbidity and mortality associated with the brain and spine surgeries has drastically decreased in last two decades. Treatment of benign brain and spinal cord tumors is done by surgical excision, whereas, in case of malignant brain and spinal cord tumors, either chemotherapy or radiation therapy is required, in addition to surgery.
Common benign tumors of brain are meningioma, acoustic neuroma, schwannoma and pituitary tumors. Pituitary tumors can be removed through nose with endoscope or microscope without opening the skull.
Generally surgery is suggested for the following in case of brain tumors Need for surgery:
- Diagnosing the type and size of tumor
- Excision of the tumorous cells
- Removal of part of tumor to slow its growth and improve symptoms
- Relieving symptoms such as build-up of cerebrospinal fluid
- Assisting in chemotherapy
Some surgical techniques include:
Craniotomy:
Cranioplasty surgery is the most common surgical procedure for excision of brain tumor. An area of the bone is cut out from the skull, the tumor is removed. The whole process is guided by MRI or CT scans either before the surgery or during the surgery.
Neuroendoscopy:
It also called keyhole brain surgery is done by making small opening in the brain with the aid of endoscope. Neuroendoscopy enables neurosurgeons to access areas of the brain that cannot be reached with traditional surgery and remove the tumor without cutting or harming other parts of the skull. The procedure is performed using an endoscope, a small telescope-like device equipped with a high-resolution video camera and eye piece on the end to allow the neurosurgeon to navigate and access the tumor.
At Wockhardt Hospitals we have a dedicated team of neurosurgeons, medical oncologists, paediatric oncologists and radiation oncologist specialised in Neurooncolgy. The specialists also use latest operative advances with navigation, advanced surgery techniques and neurophysiology monitoring .
For more information on brain tumors symptoms, diagnosis and treatment contact our neurosurgery department at Wockhardt hospitals.