Home » Medical Procedure » Myringotomy Surgery
Myringotomy Surgery (Ear Tube Surgery)
Procedure & Treatment
What is
a Myringotomy?
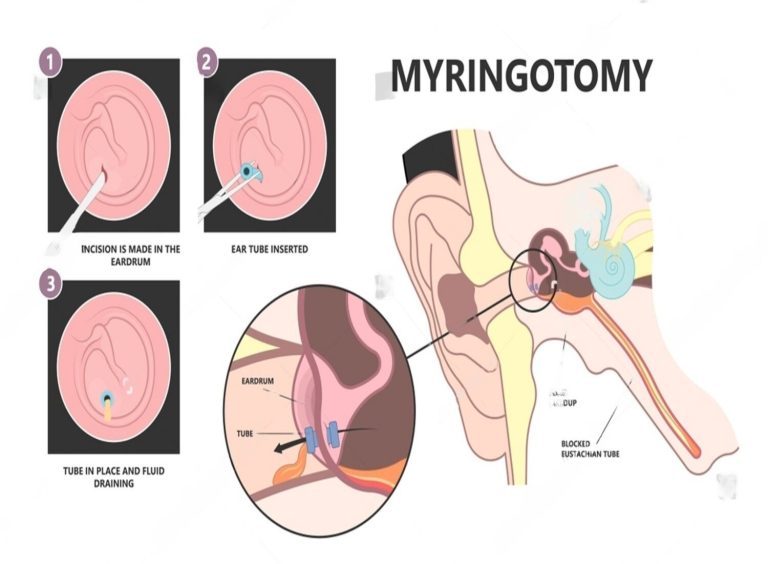
Myringotomy is performed on the Tympanic membrane (also known as the eardrum. The surgery is performed by an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist to drain the fluid (which can be classified as serous, mucoid, or purulent) from the middle ear. It can be done in one ear or both. It is one of the most recommended surgeries to treat Otitis Media with Effusion, commonly called OME (acute and chronic).
The procedure usually involves making a small incision with a Myringotomy knife. This provides direct access to the middle of the ear. It is usually done to restore hearing abilities caused by chronic fluid buildup, treat ear infections, and take sample fluid from the ear for lab tests.
Signs & Symptoms of Myringotomy
Myringotomy is more common in children than adults. Here are four signs that you need Myringotomy –
- Frequent Ear Infection - Frequent ear infections can cause severe pain and scarring to the inner parts of the ear. This can get more painful and cause the eustachian tube to become blocked and build pressure behind the eardrum. This will improve ventilation and reduce the number of infections.
- Balance Loss - Excess fluid in the ear causes many problems. It affects not only hearing but stability as well. Adequate sensory information does not reach the brain when the vestibular portion of the inner ear becomes blocked. To keep the body upright, the brain will overcompensate by learning new things or moving its eyes.
- Hearing Loss - Fluid accumulation behind the eardrum may result in hearing loss. This can result in speech stuttering and communication issues. Adult hearing loss can considerably negatively influence daily life, including work and family. Also, inner ear trauma caused due to air travel or scuba diving can require Myringotomy.
Causes of Medical Conditions that Require Myringotomy
Myringotomy is done to improve hearing ability, balance, treat infections, and remove fluid inside the ear. Here’s what causes these medical conditions-
Damage to the inner ear can be caused due to increasing age and loud noise. This causes wear and tear on the hair of the nerve cells in the cochlea that send signals to the brain. When these hairs are damaged, they fail to send an electrical signal to the brain, causing hearing loss.
After ear infection treatment, fluid remains in the middle ear for a few days, which might cause a blockage. The buildup can cause bacteria to grow and be trapped inside the ear, leading to ear infections.
Drinking water while lying on your back and a sudden increase in air pressure can also cause blockage of Eustachian tubes.
Types of Myringotomy
The following are the types of Myringotomy performed as per their procedural approach –
- A Tympanostomy is a procedure that involves cutting through the tympanic membrane or tree to allow for the constant outflow of infectious fluids from the middle ear and ear tubes.
- This procedure is carried out by an otolaryngologist or ear, nose, and throat specialist. During your child's surgery, the medical professional removes blood from the middle ear and places a little tube in the eardrum. A very small tunnel is created by the passageway connecting the middle ear with the outer ear canal. This balances the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum, preventing fluid accumulation.
Diagnosis Performed for
Myringotomy
If you are suffering from ear problems, our doctors at Wockhardt Hospitals perform a test using an Otoscope instrument. The following are the tests done before a Myringotomy –
Blood Test – By measuring the blood level of the protein Prestin, a simple blood test can identify inner ear injury and estimate the degree of hearing loss. It is also done to rule out any autoimmune diseases.
- Hearing Test - Hearing tests are primarily used on adults, while others are utilized on infants, kids, and adults. Types of hearing tests include -
- Pure-Tone Testing - This common hearing test determines what pitch you can hear at the quietest volume. Pure-tone testing is done on both adults and children.
- Bone Conduction - This testing is performed to determine if your outer or middle ear is blocked by wax or fluid or whether you have hearing loss in your sensory cells.
- Speech Testing - This type of hearing test may be administered to adults and some youngsters. The listening and repetition of specific words is a part of speech testing. The test reveals how well you comprehend speech.
- Otoacoustic Emissions Test (OAE) - Audiologists perform this examination to assess the operational features of your inner ear.
Tympanometry – This examination measures the flexibility of your eardrum. Audiologists may perform tympanometry tests to check for a ruptured eardrum, fluid in the middle ear, or wax in the ear canal.
Myringotomy
Procedure
The primary aim of a Myringotomy surgery is to enable the drainage of fluid that has become trapped in your middle ear. This substance may be blood, pus, or water. Myringotomy is performed for chronic fluid accumulation and middle ear inflammation due to the following reasons –
- Avert further ear infections
- Alleviating pressure-causing pain
- Treatment for the problem is not working.
- Prevent either temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Here’s how Myringotomy surgery is done –
- In most cases, a local anesthetic can be used to perform a Myringotomy surgery.
- An eardrum incision is made after the ear canal is numbed and cleaned to drain the middle ear fluid.
- To maintain this opening, an ear tube is placed.
- Next, to stop any bleeding, cotton is wrapped around the ear.
Before
Procedure
Before the surgery, you will be called for a final consultation, where the doctors will discuss the condition and what to expect after the surgery. On the day of the surgery, you are supposed to visit the hospital before time in case additional tests are needed. Generally speaking, the evening before your Myringotomy procedure, you shouldn’t eat or drink anything after midnight. Additionally, you’ll need to bring along a reliable friend or family member to pick you up and drop you off at your appointment.
Young teens, kids, and newborns need a brief general anesthetic before the surgery, and adults can have the Myringotomy technique done as an outpatient operation using phenol and topical Lidocaine.
After
Procedure
The patient is given antibiotic ear drops following surgery. After the procedure, the patient is called for a follow-up visit. The best antibiotics can be chosen using cultures that were obtained after surgery. Tympanostomy tube placement should be done in addition to Myringotomy for children with effusions or otitis media resistant to Myringotomy alone. Usually, the tympanic membrane heals on its own. If otitis persists, a second Myringotomy or the placement of ear tubes may be necessary. After a Myringotomy procedure, your ear may feel congested. Your hearing may not get better immediately; this is a common adverse effect.
You will receive comprehensive postoperative instructions from your surgeon. You must strictly adhere to the following recommendations to guarantee a successful recovery. Generally, you ought to –
- Take all prescription drugs exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Replace your gauze frequently.
- Keep your head out of the water.
- When taking a shower or a bath, wear earplugs.
Myringotomy Treatment
You will be able to return home that day. After one to two days, you should be able to resume your regular activities—aside from swimming. You should also be able to quickly return to your normal activities with the support of regular exercise. Also, avoid bathing without earplugs. Before exercising, seek guidance from the medical staff or your doctor. The Myringotomy tube will naturally dislodge in your ear after 6 to 18 months, depending on the grommet’s construction and composition.
Risk Factors for
Myringotomy
Generally, the risks or possible complications after this surgery are very low at Wockhardt Hospitals, as we have the most experienced surgeons working in conjunction with a multidisciplinary team of medical experts. Typical risk elements include-
- Age - Due to their thin and straight Eustachian tubes and a higher incidence of adenoid infections, children typically between 6 months and 12 years are at a greater risk.
- Bottle Feeding in Children - Bottle feeding, typically done while lying down, is a common risk factor for otitis media.
- Children in Daycare - Children in daycare are at heightened risk because colds and the associated ear infection may easily transfer from one kid to another.
- Seasonal Variation - The risk of otitis media rises during the winter and rainy months when colds and flu are more prevalent.
- External Factors - Extended exposure to harmful smoking or other air pollutants raises the likelihood of developing otitis media.
Life Wins Stories
The vision and leadership of Wockhardt’s Founders have been instrumental in shaping the organisation’s ethos of providing high-quality and affordable healthcare services to patients worldwide. Read and listen to the heartfelt experiences of our patients as they share their stories about the exceptional care they received at Wockhardt Hospitals.


Paresh Vyas
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.

Meena Kothari
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.
Life Wins Stories

Paresh Vyas
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.

Meena Kothari
Excellent facility with renowned Cardiologists like Dr Dharmesh R Solanki. Very humble doctors, and good staff. Value for money.
FAQs on Myringotomy Surgery
Q. Does myringotomy improve hearing?
A myringotomy procedure is performed to drain out fluid trapped inside the middle ear, which could be water, pus, or even blood. Since these elements can cause reduced hearing in patients, after a myringotomy surgery, their hearing can be restored and improved.
Q. What is the success rate of myringotomy?
Myringotomy procedure for hearing loss has a success rate of about 94%, showing restoration in hearing among adults and children alike. However, it’s generally recommended for patients with hearing problems due to fluid accumulation in their middle ear.
Q. What is the difference between myringotomy and tympanoplasty?
A myringotomy is making a tiny incision in the eardrum to release pressure or drain fluid such as pus or blood. Sometimes, a tube is inserted to maintain the continuous draining. In contrast, tympanoplasty is a surgical treatment that involves grafting tissue onto the tympanic membrane in order to heal a ruptured eardrum or restore hearing function.
Q. What is the purpose of myringotomy?
Myringotomy is a treatment for persistent ear infections or fluid accumulation behind the eardrum. A hole must be made in the eardrum to let fluid trapped in the middle ear drain out. To help maintain drainage, a little tube is frequently placed into the eardrum’s opening. This fluid might be water, pus, or blood.
Q. What to expect after a myringotomy?
Following a myringotomy, patients could feel lightheaded, have transient ear discharge, or both. At first, pressure alleviation may help with hearing. Recovery usually entails adhering to post-operative care recommendations and avoiding getting water in the ears. You will receive a comprehensive set of instructions from your surgeon after surgery. To guarantee a full recovery, you must strictly adhere to the given instructions. The majority of people recover completely in four weeks or less. If you have ear tubes inserted, they ought to come out on their own in six to twelve months.
Q. Is Myringotomy a major surgery?
Myringotomy involves a small incision, which makes it a less invasive surgery. It is done to relieve ear infection that causes pain and irritation.
Q. What are the advantages of Myringotomy?
There are a lot of possible advantages of Myringotomy. Myringotomy, for instance, can –
- Lower ear infections.
- Restore hearing loss brought on by fluid accumulation.
- Reduce ear pressure and pain.
- Boost your equilibrium.
- Children’s academic & speech development.
Q. Is Myringotomy surgery painful?
Pain is eliminated during Myringotomy surgery by anesthesia. However, you can feel some minor discomfort or pain after your surgery. To relieve discomfort, take over-the-counter painkillers. Your surgeon may also administer numbing ear drops. Take all drugs exactly as prescribed.
Q. What are the complications of Myringotomy surgery?
The surgical procedure known as Myringotomy carries considerable hazards. Potential issues include:
- Ear canal damage that requires surgery.
- Damage to your eardrum.
- Bleeding excessively.
- Infection.
- Draining over time.
- Sensitivity to anesthesia.
- A non-healing, permanent hole in your eardrum.
- Eardrum hardening, which may lead to hearing issues.
Q. Who needs Myringotomy?
When fluid buildup in the middle ear, myringotomies are carried out on both adults and children. There are several potential causes, including –
- Severe or persistent ear infections
- Injury-related ear bleeding
- Changing air pressure causes ear pain
- A torn eardrum