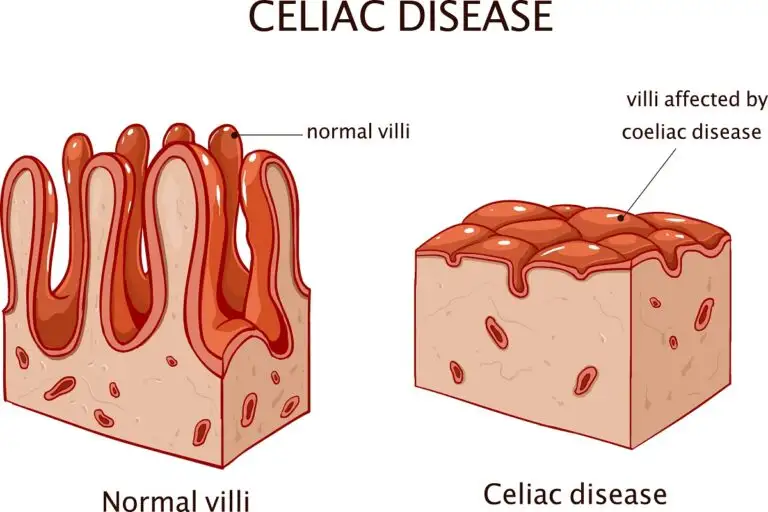
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which your immune system responds abnormally to gluten. Gluten is present in wheat, barley, and rye. If you have a gluten allergy, eating gluten will cause your immune system to destroy your villi. These are the finger-like parts of your small intestine that are responsible for absorbing nutrients.
Without healthy villi, you won’t be able to get the nutrition that you need. This can lead to malnutrition. Gluten Allergy can have serious health consequences, including permanent intestinal damage.
Adults and children often experience different symptoms due to celiac disease. Children will most commonly have digestive symptoms. These can include:
- abdominal bloating and gas
- chronic diarrhoea
- constipation
- pale, foul-smelling stool
- stomach pain
- nausea and vomiting
The failure to absorb nutrients during critical years of growth and development can lead to other health problems.
These can include:
- failure to thrive in infants
- delayed puberty in adolescents
- short stature
- irritability in mood
- weight loss
- dental enamel defects
In Adults may also have digestive symptoms if they have celiac disease. However, adults are more likely to experience symptoms such as:
- fatigue
- anemia
- depression and anxiety
- osteoporosis
- joint pain
- headaches
- canker sores inside the mouth
- infertility or frequent miscarriages
- missed menstrual periods
- tingling in the hands and feet
If you think you might suffer from a gluten- or wheat-related condition, then it’s important that you talk to a gastroenterologist before diagnosing yourself or beginning any treatment on your own. An allergist or can run tests and discuss your history with you to help reach a diagnosis.
Celiac disease can lead to severe health complications, especially in children.
Because there’s a genetic component to celiac disease, it can run in families as well.
To diagnose celiac disease or wheat allergy , your doctor will need to conduct a blood or skin prick test. These tests are dependent on the presence of gluten or wheat in your body in order to work.
Managing gluten deficiency:
The treatment for celiac disease is adhering to a strict gluten-free diet . The treatment for a wheat allergy is to adhere to a strict wheat-free diet.