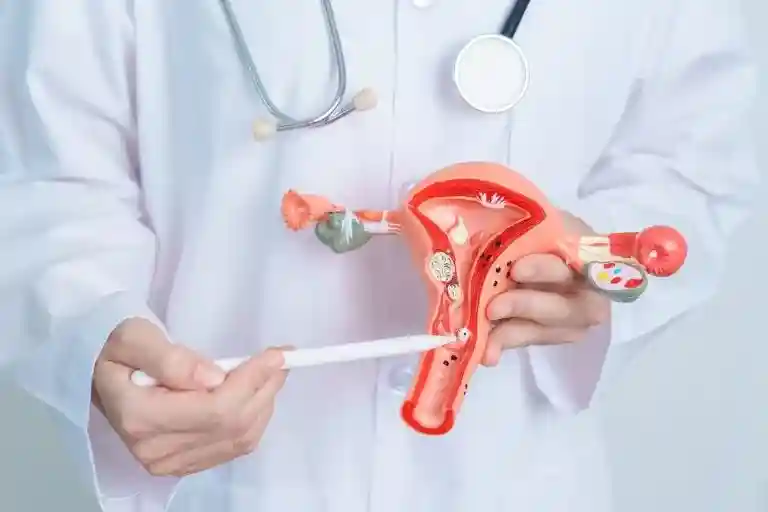
Cervical cancer is the growth of aberrant cells in the body part called the cervix (the lower section of the uterus connecting to the vagina). These cancers are caused by several strains of human papillomavirus (in short, HPV), which is a sexually transmitted viral pathogen. When a human body is exposed to HPV, the immune system of the body creates resistance and does not let the virus harm the body. Thus, the virus can live for a longer period in the human body, which contributes to the process that causes cancer cells to grow in the cervix.
As this condition might be deadly, it is important to see a doctor immediately upon experiencing the first symptom, such as – vaginal bleeding, water and bloody vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, and heavy menstrual bleeding. The symptoms are quite similar to PCOS – hence, it is important to visit the doctor at the earliest. The doctor will perform some cervical cancer diagnosis to determine what type of cancer you have and where the cancer has spread. With the help of a diagnosis report, the doctor will plan a treatment that will suit your needs.
How is Cervical Cancer Diagnosed?
Cervical cancer diagnosis consists of several tests, as mentioned below –
Screening – Screening tests can help detect precancerous cells in addition to cervical cancer. Most doctors usually recommend this after the age of 21, which can be done every few years. Screen tests include –
- Pap Test – During a pap test, a healthcare provider scraps and brushes cells from the cervix that are examined to check for abnormal cells. In addition to detecting cancer cells, it can also detect the changes in the cell, which shows the risk of cancer.
- HPV DNA Test – The HPV DNA test includes testing cells from the cervix for infection with any of the variants of HPV that are most likely to lead to cervical cancer.
When the doctors suspect cervical cancer during the pap or HPV DNA tests, they might order tests to thoroughly examine the cervix using a colposcope – a special magnifying instrument. During the examination, the doctor removes a part of the cervical cells using two processes –
- Punch Biopsy – During a punch biopsy, the doctors pinch off a small sample of cervical tissue using a sharp tool.
- Endocervical Curettage – This uses a small spoon-shaped instrument called a curet to scrape off cervical tissue for examination.
If the test results are concerning, the doctors might order more diagnostic tests, such as –
- Imaging Tests – Imaging tests such as CT Scan, MRI, PET Scan, etc., are done to locate the position of the cancer, in addition to understanding the size of the cancer.
- Visual Examination of the Bladder – The doctor uses a special scope to look for the signs of cancer in the rectum and bladder.
- Electrical Wire Loop – This uses a thin, low-voltage wire to get a small sample of tissue and is usually done at the doctor’s chamber. They might numb the area to avoid any discomfort. This test is sometimes known as the loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP).
- Cone Biopsy – This test is also known as conization, which helps doctors harvest deeper layers of cervical cells for testing. The doctor might give you anaesthesia to lessen or avoid discomfort.
How is Cervical Cancer Treated?
Cervical cancer treatment involves several treatment processes depending on the type, size, and location of the cancer. Here are some of the most frequently used treatment methods for cervical cancer –
- Radiation Therapy – Radiation therapy uses energy beams to kill cancer cells, which come from protons, x-rays, or any other sources. It is usually combined with chemotherapy as the primary cervical cancer treatment if the cancer has spread to the outside of the cervix. Radiation therapy can either be given internally (brachytherapy), externally (External Beam Radiation Therapy), or both.
- Chemotherapy – During chemotherapy, the doctors give strong medicines to ensure all the cancer cells die. Low doses of chemotherapy are usually combined with radiation to kill cancers that have spread in the surrounding region of the cervix. However, higher doses of chemotherapy are given to control symptoms of advanced cancer. It is also used before the surgery to shrink the size of the cancer.
- Targeted Therapy – Every cancer cell has some chemical, and in targeted therapy, medicines are given to target the specific chemicals in the cancer cells. The medicines block the chemical, which causes the cancer cell to die. Usually, doctors combine the targeted therapy with chemotherapy for advanced cervical cancer treatment.
- Immunotherapy – Cancer cells are good at hiding from the immune system, thus surviving in the human body. Immunotherapy involves giving medicines to cancer patients to help the immune system find and kill these cancer cells. The immune system fights off the disease by attacking germs and other foreign cells. This is done when all other treatments for cervical cancer are not working.
Is Surgery a Viable Option for Cervical Cancer?
Surgery is used only to treat cancers that are small and haven’t grown beyond the cervix. Several other factors determine if cervical cancer surgery is the best treatment for the patient, such as –
- Size of the cancer
- Location of the cancer
- Age of the patient
- Stage of the cancer
- If they want to become pregnant in future
Here are some surgical options the doctors might use for cervical cancer treatment –
- Surgery to Cut Away the Cancer – This is done for a very small cervical cancer. Also, it might be possible to cut away all the cancer during a cone biopsy. During cervical cancer surgery, the doctors cut away the cone-shaped cervical tissue, leaving the remaining tissue intact. This is the best option if the patient plans to be pregnant in future.
- Trachelectomy – This surgery might be done to treat small cervical cancer, in which the doctors remove the cervix and the surrounding tissue.
- Hysterectomy – Most of the time, cervical cancer does not spread beyond the cervix, which is treated with a hysterectomy operation. This involves removing the cervix, uterus, lymph nodes, and some parts of the vagina. This process might often cure the cancer and also ensure it does not come back.
Conclusion
It is important to see a doctor once the patient starts experiencing symptoms of cervical cancer. The earlier it gets detected, the better the chances of its complete treatment. Cervical cancer diagnosis is usually done depending on the type of cancer a patient is having. Once done, the concerned oncologist will chart out an effective treatment plan.
Before the cervical cancer treatment begins, it is important to discuss the goals and possible outcomes, side effects, etc., to ensure everything is carried out as planned. Visit the Wockhardt Hospitals, also known as the best cervical cancer hospital in India today to receive the best cervical cancer treatment from highly experienced and board-certified oncologists and oncosurgeons.
FAQs on Cervical Cancer Treatment in India
Q. What causes cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is mostly caused by persistent infection with specific strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) virus.