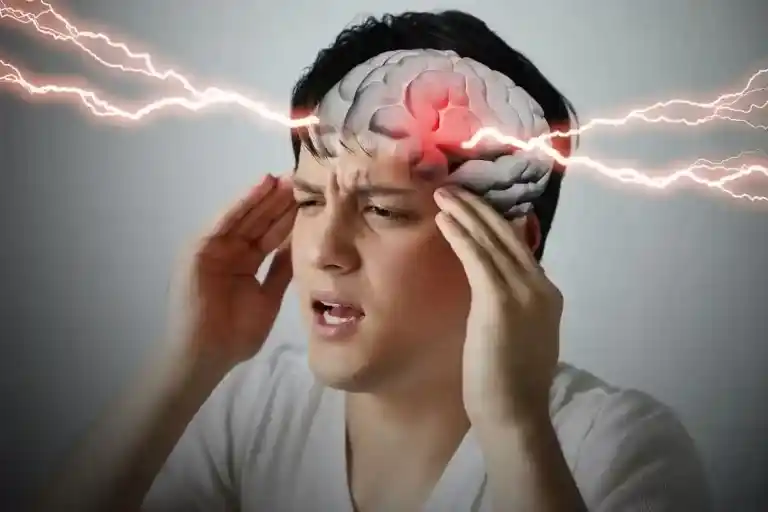
Brittle diabetes is a rare and severe form of diabetes that poses unique challenges for both patients and healthcare professionals. It is a particularly challenging and less well-known subtype of Diabetes, which itself is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is sometimes referred to as labile or unstable diabetes because of the possibility of significant and frequent blood sugar changes. Brittle diabetes patients experience significant swings in their blood glucose levels. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) episodes may occur often as a result of the fluctuations. These unpredictable changes can lead to a variety of complications and make daily life exceedingly challenging for those affected with brittle diabetes, also known as labile or unstable diabetes.
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes are most likely to develop brittle diabetes (with Type 1, the body does not manufacture insulin). It most commonly affects women in their 20s and 30s for unexplained causes.
Causes of Brittle Diabetes
Understanding the brittle diabetes causes is essential for effectively managing and treating this complex condition. The brittle diabetes causes are multifactorial and can vary from person to person:
- Insulin Sensitivity – Some individuals with brittle diabetes have an extraordinarily high sensitivity to insulin, meaning that even small adjustments in their insulin dose can lead to significant blood sugar fluctuations.
- Gastroparesis – Gastroparesis is a condition in which the stomach’s ability to empty food into the small intestine is impaired. In individuals with brittle diabetes, delayed gastric emptying can lead to erratic blood sugar levels since the timing of food digestion and absorption becomes unpredictable.
- Celiac disease – An autoimmune reaction is brought on by gluten, a protein present in certain grains, in celiac disease patients. When untreated, celiac disease is associated with increased hypoglycemia and other problems of diabetes.
- Dietary Factors – Inconsistent eating habits or the consumption of foods with varying glycemic indexes can contribute to blood sugar fluctuations.
- Hormonal Changes – Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during the menstrual cycle, can influence blood sugar levels in individuals with brittle diabetes.
- Psychological Factors – Stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors can have a profound impact on blood sugar levels. The emotional toll of living with brittle diabetes can make it even more challenging to manage.
- Medication or Insulin Regimen – The choice of insulin type, the method of administration, and the timing of insulin doses are critical in managing brittle diabetes. Changes in medication or insulin regimens can lead to unstable blood sugar levels.
- Certain comorbidities – Comorbidity is the simultaneous presence of two or more medical disorders in one individual. If they also have gastroparesis or celiac disease, they are more likely to develop brittle diabetes.
Brittle Diabetes Symptoms
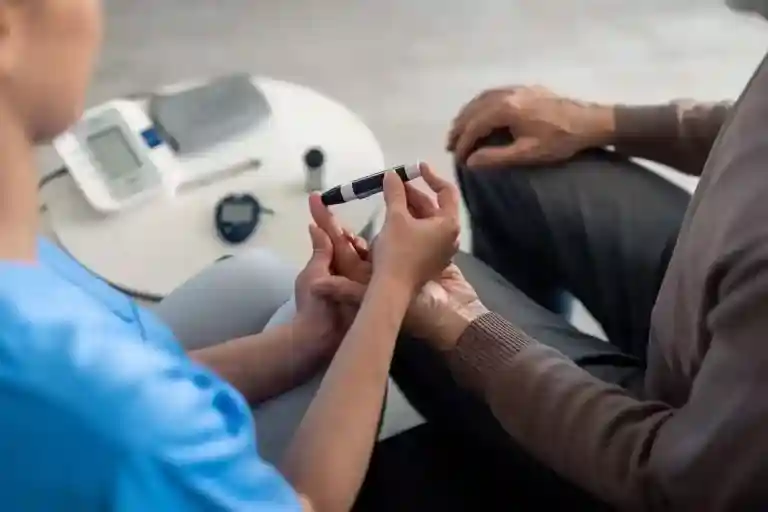
Recognizing the brittle diabetes symptoms is crucial in seeking early diagnosis and effective brittle diabetes treatment. Some people are unable to detect hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia when it occurs in their bodies.
Signs of Hypoglycemia
Individuals with brittle diabetes often experience episodes of low blood sugar, which can lead to brittle diabetes symptoms like shakiness, sweating, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Hypoglycemia affects people differently. The following are typical warning symptoms of excessively low blood sugar:
- Mood changes, such as feeling nervous, anxious, or irritable
- A fast heartbeat
- Shaking, sweating, or chills
- Feeling dizzy or might pass out
- Confusion
- Emotional instability
- Hunger
- Nausea & Vomiting
The symptoms of hypoglycemia that worsen with time include:
- Headaches
- Feeling sleepy or weak
- Pale complexion
- Vision changes
- Tingling sensation in the lips, tongue, or cheeks
- Seizures
Signs of Hyperglycemia
Compared to hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia’s symptoms might be less severe.
- Increased thirst
- Urinating more often than usual
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially fatal condition that can develop from untreated high blood sugar, is one such possibility. When someone has DKA, their liver creates acids known as ketones. In the body, these acids can accumulate to dangerous levels.
Signs of DKA
- Fast breathing
- Sweet-smelling breath
- Dry mouth
- Abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Flushed face
- Muscle stiffness
- Drowsiness
Treatment of Brittle Diabetes
Managing brittle diabetes is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The primary goals of brittle diabetes treatment are to stabilize blood sugar levels, prevent severe fluctuations, and reduce the risk of complications.
Here are some key components of brittle diabetes management at Wockhardt Hospitals:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) – CGM systems track blood sugar levels in real time, providing valuable data to help patients and healthcare providers understand patterns and triggers for fluctuations.
- Insulin Pumps – Daily injections can be substituted with an insulin pump. Insulin pumps offer precise control over insulin delivery, allowing for customized basal and bolus insulin doses. It can help individuals with brittle diabetes achieve more stable blood sugar levels.
- Gastroparesis Management – Treating gastroparesis, if present, may involve dietary modifications and medications to improve stomach motility.
- Islet Cell Transplantation – This procedure involves injecting healthy insulin-producing cells into the liver from the pancreas of a deceased patient.
- Pancreatic Transplant Surgery – To increase insulin production, the patient’s pancreas is replaced with the pancreatic of a dead donor.
- Frequent Glucose Monitoring – Frequent monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for identifying patterns and making necessary adjustments to the brittle diabetes treatment plan. These monitors have alarms and safety alerts to warn of growing or falling levels before they become too problematic.
- Psychological Support – Managing the psychological aspect of brittle diabetes is crucial. Psychotherapy and stress management techniques can help individuals cope with the emotional toll. The long-term management of diabetes has shown to be particularly responsive to psychotherapy.
- Lifestyle Changes – Regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and consistent sleep patterns can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Medication Adjustments – For individuals with type 2 diabetes who are using oral medications, adjustments to their medication regimen may be necessary to achieve better blood sugar control.
- Specialized Therapies – Treatment options for patients whose brittle diabetes is brought on by emotional stress, an eating problem, or depression may include specialized therapy.
Why choose Wockhardt Hospitals for the management of Brittle Diabetes?
The complicated and difficult disease of brittle diabetes calls for specialized treatment and a holistic approach to management. For people looking for the best care for this rare but difficult disease, Wockhardt Hospitals are a great option since they offer a thorough and patient-centered approach to treating brittle diabetes and diabetes surgery. They strive to continue to lead medical innovations. The hospital participates in clinical research and keeps up with the most modern advances in the management of diabetes in order to offer the best care possible.