Insulin resistance is a metabolic condition that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its association with various health problems, including obesity, Type-2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. It revolves around the hormone insulin, which is essential in controlling blood sugar levels. It is a complicated yet critical part of human physiology.
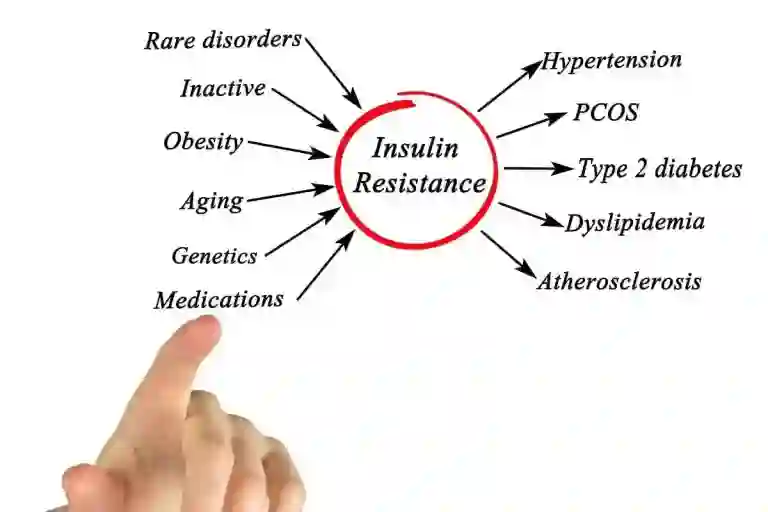
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the fat, muscles & liver cells do not respond to insulin as expected and are, therefore, unable to use blood glucose for energy. The pancreas produces an extra amount of insulin to make up for the loss, and the levels of blood sugar rise over time. Below are the various factors to consider.
Insulin Resistance Symptoms
Insulin resistance is often referred to as a “silent” condition because it can develop slowly and progress without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition worsens, variousinsulin resistance symptoms may become evident. It is important to be aware of these symptoms as early detection and intervention can help prevent the development of more severe health problems. Some common symptoms of insulin resistance include:
- Increased Hunger – People with insulin resistance often feel hungry more frequently, even shortly after eating. This increased appetite can contribute to overeating and further weight gain.
- Weight Gain – Many individuals with insulin resistance experience unexplained weight gain, especially around the abdominal area. This is often due to the body’s inability to efficiently use glucose for energy, leading to the storage of excess fat.
- Frequent Urination – As the body struggles to control blood sugar levels, frequent urination may occur as the kidneys attempt to eliminate excess glucose from the bloodstream.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Women with insulin resistance are at a higher risk of getting PCOS, which can cause irregular periods, vaginal pain, infertility, and other health concerns.
- Skin Changes – Skin issues, such as dark patches on the neck or in the armpits (Acanthosis Nigricans), can be indicative of insulin resistance. These changes are linked to hormonal imbalances associated with the condition.
- High Blood Pressure (BP) – Insulin resistance can lead to elevated blood pressure (BP), which is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- Chronic Fatigue – It is a common symptom of insulin resistance, often related to the body’s inability to effectively utilize glucose for energy production.
- Loss of Hands and Feet Sensation – This is a sensory symptom. Blood circulation is impacted when the level of sugar rises because of insulin resistance, and signaling to sense or feel is hampered. In the latter phases, the patient might fully lose the sensation and feeling.
- Frequent Infections – The body’s capacity to repair wounds declines as sugar levels rise. People become more susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections as a result.
- High Triglycerides – Increased levels of triglycerides in the blood are often seen in individuals with insulin resistance. High triglycerides are an established risk factor for heart disease.
- Gestational Diabetes – Pregnant women with insulin resistance may develop gestational diabetes, which can have adverse effects on both the mother and the baby if left unmanaged.
- Type 2 Diabetes – Perhaps the most concerning consequence of insulin resistance is the high risk of developing Type-2 diabetes. Over time, the body’s inability to respond to insulin can lead to persistently elevated blood sugar levels, a hallmark of diabetes.
Insulin Resistance Causes
Insulin resistance is a multifaceted condition with various contributing factors. While genetics can be a possible cause, lifestyle choices are often the primary drivers of insulin resistance. Some common insulin resistance causes include:
- High-carbohydrate diet – Insulin resistance is more likely in those who consume a lot of lipids and carbs, especially saturated fats. Consuming too many carbs and lipids can cause the body to store fat, especially in the liver and muscle. The body’s capacity to utilize insulin effectively may be hampered by this.
- Obesity – Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat around the abdomen, is a key factor in the development of insulin resistance. Fat cells release inflammatory substances that can impair insulin’s action.
- Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of daily exercise and a sedentary lifestyle can reduce the body’s sensitivity to insulin. Regular exercise helps improve insulin responsiveness.
- Genetics – A family history of insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes can increase an individual’s susceptibility to the condition. Genetic factors can influence how the body responds to insulin.
- Inflammation – Chronic inflammation in the body can hinder insulin function. Inflammatory processes can be triggered by conditions such as autoimmune disorders or excessive stress.
- Poor Sleep Pattern – Inadequate or poor-quality sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, including the hormones that regulate blood sugar, contributing to insulin resistance.
- Medications – Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and antipsychotic drugs, can interfere with insulin sensitivity.
- Environmental Toxins – Some environmental toxins, such as those found in pesticides and pollutants, have been linked to insulin resistance.
Insulin Resistance Brought on by Hormonal Issues
Our body’s ability to utilize insulin can be impacted by problems with certain hormones. Among the hormonal conditions that might result in insulin resistance are:
- Cushing’s Syndrome – This syndrome develops when there is too much cortisol in the body. Insulin resistance can result from elevated cortisol levels, which work against insulin’s actions.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – PCOS is a condition that affects hormone levels in women, often leading to insulin resistance.
- Hypothyroidism – The thyroid becomes underactive and stops producing adequate thyroid hormone, resulting in this disease. It causes a slowdown in metabolism, which might result in insulin resistance and slow down glucose metabolism.
Insulin Resistance Treatment
The goal of insulin resistance treatment is to increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, control blood sugar levels, and lessen the hazards to one’s health. Adopting a thorough strategy that incorporates dietary adjustments and, in certain situations, medicinal treatments is essential. The insulin resistance treatment that are mainly used are listed below:
- Dietary Changes – A well-balanced, nutritious diet is paramount in managing insulin resistance. Aim for a diet that includes a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing the consumption of refined carbs and added sugars can stabilize blood sugar levels. Fiber helps slow down the glucose absorption, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Regular Exercise – Physical exercise is a great technique for increasing insulin sensitivity. Both aerobic exercise & strength training can help manage weight, lower blood sugar, and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
- Weight Management – Achieving & maintaining a healthy weight is critical in addressing insulin resistance, as excess body fat is a primary driver of the condition. Managing portion sizes can assist in weight management, reducing the strain on the body’s insulin response.
- Stress Reduction – High-stress levels can negatively impact insulin sensitivity. Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help reduce stress and improve hormonal balance.
- Sleep Hygiene – Prioritizing good sleep habits can positively affect insulin sensitivity. Spend 7-9 hours each night getting a good deep sleep.
- Medications – In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to manage insulin resistance, such as Metformin. These medicines can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar – Regular monitoring of blood sugar can help individuals with insulin resistance understand how their diet and lifestyle choices affect their condition. Also, Consult with a healthcare provider who can provide personalized guidance and diabetes treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Why is Wockhardt Hospital considered the Best for the Treatment of Insulin Resistance?
Wockhardt Hospitals has a great reputation in India as a prominent healthcare center, providing comprehensive and innovative care for those suffering from insulin resistance and associated disorders. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities, enabling accurate and timely diagnosis for insulin resistance treatment. The hospital offers a comprehensive range of services, from dietary counseling and exercise therapy to medication management and surgical interventions when necessary. This multifaceted approach ensures that patients receive well-rounded care.