What is a 2D Echo Test?
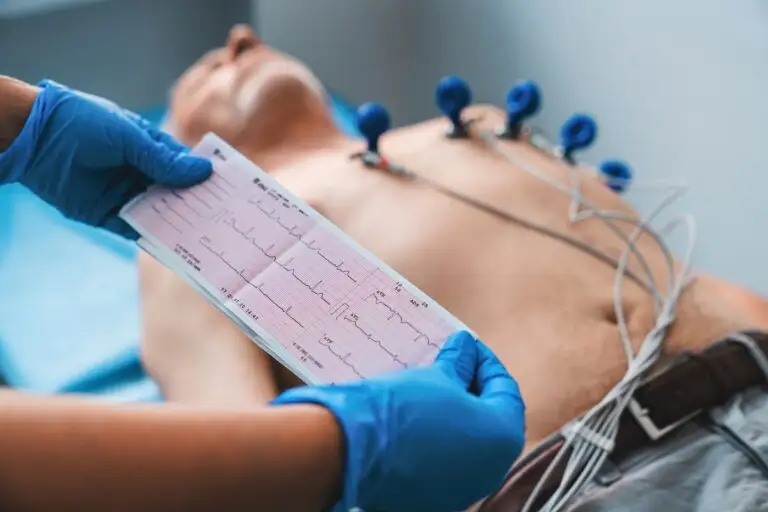
A 2D echocardiography test is as good as sonography of the heart and is a quite common cardiac investigative tool. It is a non-invasive, painless, and risk-free procedure for the heart. The procedure, uses high-frequency ultrasound waves, reflecting off various structures of the heart, to obtain one- and two-dimension real-time images of the beating heart. It assists, to visualize and assess heart muscles, valves, blood flow, four-chamber dilatation, and overall heart functioning capacity.
Moreover, the test can be done on an outpatient basis in a clinic. It takes around 20 to 30 minutes for the test to be done. During the test, the patient lies down and a probe will be placed on the chest to create pictures of the heart which is viewed on a screen monitor. Thereafter printouts, the images are then given to the doctor and the patient as a report. The test offers, the cardiologist valuable information regarding the function and health of the heart.
Generally, the cardiologist will advise the investigation in order to ascertain a diagnosis of an underlying heart condition when a patient has the symptoms such as breathlessness, chest pain, giddiness, and extreme fatigue. The 2D echo test can also be carried out in case a patient has a history of any cardiac condition such as heart blockages or previous heart attack.
The 2D echocardiography investigation can determine whether there is heart failure, coronary artery disease, irregular heartbeats, valvular damage, cardiomyopathy, and infections in the heart. These circumstances, coincide with the symptomology that the patient presents to the cardiologist.
There are various heart conditions, which can be derived from the result of the 2D echo which can be the cause of heart damage or failure:
-
- Blood clots and arterial damage result from atherosclerosis due to clogging of the arteries.
-
- Congenital Heart Disease brought about by defects in one or more of the heart structures during birth
-
- General Cardiomyopathy triggers enlargement of the heart due to thick or weak heart muscle
-
- Heart Failure is due to muscle too weak or stiffness during heart relaxation due to which blood cannot be pumped efficiently.
-
- It is an excellent diagnostic tool to confirm old heart attacks, and ongoing attacks, and can predict future myocardial infarction as well. Besides this, the test can also determine the percentage of heart blockages.
-
- Pericarditis. An inflammation or infection of the sac that surrounds the heart.
-
- Pericardial effusion or tamponade. The sac around the heart can become filled with fluid, blood, or infection. This can compress the heart muscle and prevent it from beating and pumping blood normally.
-
- Atrial or septal wall defects.
- Other conditions that can be determined are murmurs due to valvular conditions or tumors and infections of the heart valves.
There are Three Basic “modes” used to Image The Heart:
-
- Two-dimensional (2D) imaging
-
- M-mode imaging
-
- Doppler imaging
Types of 2D Echo Test:
-
- Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): It is done to get a more detailed picture of the heart. It may be advised to look for blood clots in the heart. A small transducer is attached to a flexible tube. The tube is guided from the mouth, down the throat, and into the esophagus. The heart functioning can be then assessed closely through the transducer.
- Stress Echocardiography: In this test, the heart is made to beat faster by making the patient walk on the treadmill or ride a stationary bicycle. The technician will use echo to create images of the heart before the exercise and as soon as the patient finishes the exercise. Some diseases like coronary heart disease are better diagnosed by a stress echo test.
- Fetal Echocardiography: Fetal echo is used to examine the unborn baby’s heart. It is usually done at about 18 to 22 weeks of pregnancy.
- 3D Echocardiography: A three-dimensional echo creates 3D images of the heart. It gives a detailed image and a better understanding of heart structure and functioning. 3D echo may be used for planning or overseeing a heart valve surgery. It may also be used to diagnose heart problems in children.
Precautions Before the 2D Echocardiography:
-
- You do not need to avoid eating or drinking before a 2-D echo.
-
- Take your medications as you usually do.
-
- Wear anything you would like.
-
- Smoking or using any nicotine products should be avoided.
-
- Restrain from drinking coffee or anything with caffeine in it. This includes decaf drinks, which still contain a small amount of caffeine. It also includes over-the-counter medications that contain caffeine.
-
- You may need to adjust your medication schedule before your echo.
- Do not stop taking any medications or make any changes.
How Does a 2D Echo Test Work?
A non-invasive test called 2D echocardiogram, sometimes referred to as 2D echo, is used to
evaluate the sections of your heart and analyse how it is working. Using sound vibrations, this
test creates pictures of the different parts of the heart. It helps in identifying signs of damages,
obstructions, and blood flow rate.
2D Echocardiography Procedure
The procedure of 2D Echo will be done in the following steps:
-
- The patient will be told to lie down and take off all of his or her clothing, up to the waist.
-
- Before the procedure, a specific echo-gel will be administered to the chest.
-
- Electrodes will be put to the patient’s body. An ECG device will be linked to the electrodes.
- The picture of the heart can then be captured by placing and moving a transducer across the chest.
When Do you Require a 2D Echo Test?
The 2D Echo test is useful for the diagnosis and monitoring of variety of heart-related problems,
including:
-
- Measuring the size and function of the heart
-
- Identifying problems with heart valves
-
- Detecting blood clots or other cardiac irregularities.
-
- Finding fluid accumulation around the heart.
- Congenital cardiac abnormalities in newborns and babies.
Wockhardt Hospitals has a full-fledged noninvasive cardiac diagnostics department under one roof. The cardiologist and expert technicians are fully trained in performing the procedure and diagnosing various heart conditions. To understand more about the 2D echocardiography test, its price, its results, and at location near you.
To book an appointment visit: https://www.wockhardthospitals.com/get-appointments/
FAQs on 2D Echo Test
Q. What can you expect during the 2D echocardiography test?
During a 2D echocardiography test, patients would be asked to lie down on a table and a technician places specific electrodes on the chest and applies gel to the transducer, and then moves it around the chest to obtain images of the heart’s structure.
Q. What happens during the 2D echo test?
During a 2D echocardiography test, a small device, called a transducer, is carefully placed on the chest that emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the heart’ structures. These images are displayed on a screen in real-time or recorded for reviewing later.
Q. Is fasting required for a 2D echo test?
The 2D echocardiography test is a completely non-invasive test that utilises a device to produce images of the heart’s structure, so patients don’t need to fast before a 2D echocardiography test.
Q. What are the uses of the 2D echo test?
A 2D echocardiography test is used for:
- Assessing cardiac blood flow,
- Identifying blood clots,
- Detecting anomalies in the heart’s walls and valves,
- Evaluating the effectiveness of cardiac treatments, such as surgeries or interventions, and
- Continuous monitoring of patients with chronic heart conditions.
Q. What are the benefits of getting a 2D echo test?
The benefits of a 2D echocardiography test include:
- Non-invasive procedure
- Safe for monitoring heart health during pregnancy
- Assess risk for surgery
- Stress test
- Assess congenital heart problems
- Monitor the cardiac health of children
Additionally, a 2D echocardiography test is a cost-effective way to study the heart’s structure and function.
Q. What is a good 2D echo test result?
A 2D echo test reveals the presence or absence of any heart issues or atypical movements, or rhythms of the heart. A good 2D echo test result indicates the absence of any structural or functional issues of the heart that may cause the heart to function less efficiently and pump blood ineffectively.
Q. What is the normal result of a 2D echo test?
The result of a 2D echo test is expressed in terms of percentage and is an indicator of how well the heart functions in pumping blood. A normal 2D echo test result may fall within the range of 50-70%.
Q. What is the 2d echo test price at Wockhardt Hospitals?
The 2D Echo is a routine procedure that is cost-effective. At Wockhardt Hospital, 2D echo
tests cost between Rs 2500 and Rs 5000. The cost of an echocardiography test varies based on
several factors, including the type of echocardiogram conducted and the cardiologist’s level of
experience.
Q. Can a 2D echo detect heart blockage?
A 2D echo scan is unable to identify heart blockages. Doctors can see the heart’s internal
structures, such as the heart’s muscles, valves, and cardiac function, but they cannot detect
blockages in the heart. It can only identify the function of the heart muscle, and the presence of
clogged arteries can be inferred if there is any weakening in the heart tissue.
Q. Is 2D echo better than ECG?
An ECHO is preferable to an ECG because it provides more precise data on how your heart
valves are functioning. In an echocardiogram, the heart is ultrasonically scanned to provide
moving pictures that reveal the intricate anatomy and operation of the heart. When evaluating the
structure and function of the heart, ECHO is far more accurate than ECG.