Dr. Mudit Khanna at Wockhardt Hospitals, Mumbai Central has pioneered the use of Mako SmartRobotics in South Mumbai to treat arthritis of the Knee. He is the first surgeon in the region to perform Makoplasty Robotic Knee Resurfacing and has now gained significant experience with this technique.
Makoplasty: An Alternative to Total Knee Replacement
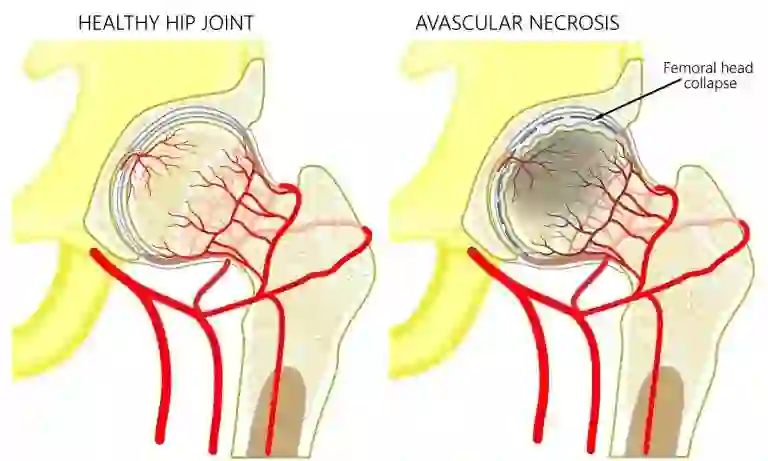
Makoplasty Robotic knee resurfacing can be an attractive alternative to total knee replacement in the appropriate patient. This technique, which involves robotic bone contouring of arthritic surfaces and customized resurfacing of the damaged area, represents an improvement over traditional or conventional partial (or unicondylar) knee replacement. Without robotic assistance, partial knee replacement can provide excellent and durable pain relief but is technically challenging, and carries a higher potential for surgical inaccuracy. Dr Mudit Khanna’s experience, combined with Mako SmartRobotic safeguards, provide an unparalleled level of accuracy, precision and personalization to optimize patient outcomes.
Advantages of Robotic Assistance in Knee Resurfacing
After robotic knee resurfacing, Dr. Khanna expects patients to return to work much faster. Compared to total knee replacement, robotic knee resurfacing provides more reliable return to select sports, a quicker and less painful recovery, a smaller incision, a more natural feeling knee, and, importantly, a lower risk of complications.
Dr. Khanna performs all his Makoplasty knee resurfacing procedures at the SOBO Unit of Wockhardt Hospitals which carries one of the lowest infection rates in the region.
Comprehensive Pain Management and Rehabilitation
Realizing the significance of Early rehabilitation and importance of Post-operative Pain management, Dr. Mudit Khanna with the help of the department of Anesthesia has established an excellent Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Program at Wockhardt Hospitals, which helps to achieve Rapid recovery after Joint Replacement Surgery by improving the quality of perioperative care with special focus on achieving excellent pain management through a multimodal pain management protocol. In addition to Dr. Mudit Khanna's expertise, the world-class environment at Wockhardt enhances the patient experience and outcome.
Schedule your consultation with Dr. Mudit Khanna today and take the first step towards a pain-free, active life with Makoplasty Robotic Knee Resurfacing!